



Comprehensive Guide to DSA Carotid Stenting (ICA)

DSA Carotid Stenting (ICA) stands for:
Carotid stenting is performed to treat carotid artery stenosis, a condition where the carotid arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis). The procedure helps:
Carotid stenting procedures are categorized based on:

Used for newly diagnosed carotid artery stenosis.
Stent placement directly opens the artery.
Common for patients with moderate to severe blockage.

Performed in patients with recurrent narrowing of the carotid artery after a previous surgery or stenting.
Stent-in-stent technique may be used.
Reduces the risk of recurrent stroke or embolism.

Balloon is inflated to widen the narrowed artery before placing the stent.
Ensures the artery remains open and stable.
Suitable for complex or severely blocked arteries.

Uses a stent coated with medication to prevent scar tissue formation.
Reduces the risk of re-narrowing.
Ideal for patients prone to restenosis.
Carotid artery stenosis may be asymptomatic in the early stages. As the blockage worsens, symptoms may include:
Mini-stroke lasting a few minutes to hours.
Temporary symptoms such as:
Sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body.
Slurred speech or difficulty speaking.
Temporary vision loss in one eye.
Dizziness or balance issues.
Sudden and severe neurological deficits.
Paralysis or weakness on one side of the body.
Confusion, speech difficulty, or cognitive issues.
Vision problems or complete loss of vision.
Abnormal sound (bruit) heard through a stethoscope.
Indicates turbulent blood flow due to arterial narrowing.
Caused by reduced blood flow to the brain.
May occur with mild exertion.
Certain factors increase the likelihood of carotid artery disease and the need for stenting:
DSA Carotid Stenting is required when narrowed carotid arteries restrict blood flow. Common causes include:
Cholesterol and fat deposits form plaques.
Gradually narrow the carotid arteries.
Neck injuries can damage the carotid artery.
May lead to narrowing or blockage.
Abnormal cell growth in artery walls.
Causes narrowing or irregularity of the artery.
After a carotid endarterectomy (CEA), restenosis can occur.
May require DSA carotid stenting.
Low-fat, high-fiber diet reduces cholesterol.
Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
Helps control weight and blood pressure.
Reduces the risk of carotid artery disease.
Improves vascular health.
Statins and antihypertensive drugs control cholesterol and blood pressure.
Reduces the risk of plaque formation.
Maintain blood sugar levels within target range.
Reduces damage to blood vessels.
Antiplatelet therapy (aspirin, clopidogrel) to prevent clotting.
Statins to lower cholesterol and reduce plaque formation.
Blood pressure control with ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers.
DSA-guided stent placement to open the narrowed artery.
Improves blood flow and reduces stroke risk.
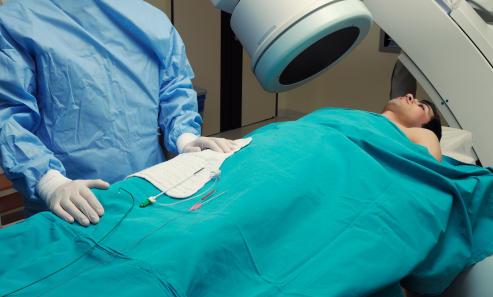

DSA maps the arteries and identifies blockages.
A catheter is inserted into the femoral artery and guided to the carotid artery.
Balloon angioplasty expands the artery.
A stent is placed to keep the artery open.
Duration: 1–2 hours.

Prevents debris from dislodging during the procedure.
Reduces the risk of stroke.

Antiplatelet medications to prevent clots.
Lifestyle modifications to prevent restenosis.

Hospital Stay: 1–2 days.
Full Recovery: 1–2 weeks.
Post-Op Instructions: